86 lines
3.3 KiB
Markdown
86 lines
3.3 KiB
Markdown
|
|
<div align="center">
|
|
<h1>regression-js</h1>
|
|
<a href="https://travis-ci.org/Tom-Alexander/regression-js">
|
|
<img src="https://travis-ci.org/Tom-Alexander/regression-js.svg?branch=master"/>
|
|
</a>
|
|
<a href="https://npmjs.com/package/regression">
|
|
<img src="https://img.shields.io/npm/v/regression.svg" alt="npm version" />
|
|
</a>
|
|
<a href="https://npmjs.com/package/regression">
|
|
<img src="https://img.shields.io/npm/dt/regression.svg" alt="npm downloads" />
|
|
</a>
|
|
<a href="https://codeclimate.com/github/Tom-Alexander/regression-js/coverage"><img src="https://codeclimate.com/github/Tom-Alexander/regression-js/badges/coverage.svg" /></a>
|
|
<br/>
|
|
<br/>
|
|
<p>
|
|
regression-js is a JavaScript module containing a collection of linear least-squares fitting methods for simple data analysis.
|
|
</p>
|
|
</div>
|
|
|
|
## Installation
|
|
This module works on node and in the browser. It is available as the 'regression' package on [npm](https://www.npmjs.com/package/regression). It is also available on a [CDN](https://cdnjs.com/libraries/regression).
|
|
|
|
### npm
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
npm install --save regression
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Usage
|
|
|
|
```javascript
|
|
import regression from 'regression';
|
|
const result = regression.linear([[0, 1], [32, 67], [12, 79]]);
|
|
const gradient = result.equation[0];
|
|
const yIntercept = result.equation[1];
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Data is passed into the model as an array. A second parameter can be used to configure the model. The configuration parameter is optional. `null` values are ignored. The precision option will set the number of significant figures the output is rounded to.
|
|
|
|
### Configuration options
|
|
Below are the default values for the configuration parameter.
|
|
```javascript
|
|
{
|
|
order: 2,
|
|
precision: 2,
|
|
}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
### Properties
|
|
- `equation`: an array containing the coefficients of the equation
|
|
- `string`: A string representation of the equation
|
|
- `points`: an array containing the predicted data in the domain of the input
|
|
- `r2`: the coefficient of determination (<i>R</i><sup>2</sup>)
|
|
- `predict(x)`: This function will return the predicted value
|
|
|
|
## API
|
|
|
|
### `regression.linear(data[, options])`
|
|
Fits the input data to a straight line with the equation 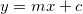. It returns the coefficients in the form `[m, c]`.
|
|
|
|
### `regression.exponential(data[, options])`
|
|
Fits the input data to a exponential curve with the equation 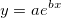. It returns the coefficients in the form `[a, b]`.
|
|
|
|
### `regression.logarithmic(data[, options])`
|
|
Fits the input data to a logarithmic curve with the equation 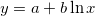. It returns the coefficients in the form `[a, b]`.
|
|
|
|
### `regression.power(data[, options])`
|
|
Fits the input data to a power law curve with the equation 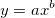. It returns the coefficients in the form `[a, b]`.
|
|
|
|
### `regression.polynomial(data[, options])`
|
|
Fits the input data to a polynomial curve with the equation 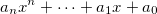. It returns the coefficients in the form `[an..., a1, a0]`. The order can be configure with the `order` option.
|
|
|
|
#### Example
|
|
|
|
```javascript
|
|
const data = [[0,1],[32, 67] .... [12, 79]];
|
|
const result = regression.polynomial(data, { order: 3 });
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Development
|
|
|
|
- Install the dependencies with `npm install`
|
|
- To build the assets in the `dist` directory, use `npm run build`
|
|
- You can run the tests with: `npm run test`.
|